Monday, February 16, 2015
Type Casting in Java
Converting one data type to another data type is known as type casting. Type Casting in Java is of two types i.e. Implicit Type Casting which is also known as Automatic Type Casting and Explicit Type Casting.
Implicit or Automatic Type Casting
- In this, smaller data type is converted to bigger data type which is also known as widening.
- There is no data loss chance.
- It is done by compiler therefore it is known as automatic type casting.
- Example: byte b=10; int x=b; Here byte type is converted to int type.
Explicit Type Casting
- In this, bigger data type is converted to smaller data type which is also known as narrowing.
- There is data loss chance.
- It is done by the user with the help of type cast operator i.e. ( ).
- Example: int x=10; byte b=(byte)x; Here int type is converted to byte type.
Type Promotion in Java
- Converting smaller data type to bigger data type is known as type promotion.
- Only promotion is allowed, demotion is not allowed.
Type Promotion Chart
- This chart tells us about the flow of converting one smaller data type to another bigger data type.
- Double can’t be converted to any data type.
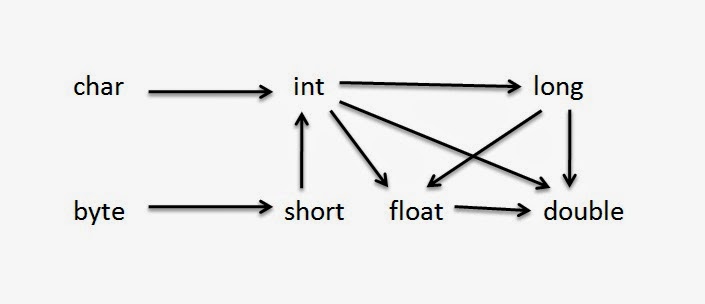
Note: Long takes 8 bytes while float takes 4 bytes, instead of that long (bigger type) can be converted to float (smaller type) which is an exception.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.